Gynecomastia Treatment
What Is Gynecomastia?
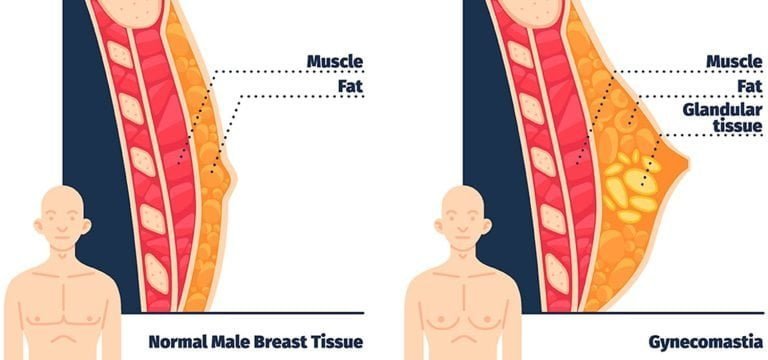
Gynecomastia (sometimes referred to as “man boobs”) is a condition of overdevelopment or enlargement of the breast tissue in boys or men. Signs and symptoms of the condition may include swollen breast tissue, breast pain or tenderness.
Causes of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia is typically caused by an imbalance between levels of the female hormone (estrogen) and the male hormone (testosterone). Some male newborns may get gynecomastia transiently while hormones from their mother are still in their bodies. The enlarged breasts usually go away within a few weeks.
Risk factors for gynecomastia include:
- Obesity: If you are overweight, you are more likely to have excess fat that can enlarge the breast tissue. Also, body fat can stimulate estrogen production and breast tissue growth. This is particularly common during puberty.
- Older age: As men get older, they produce less testosterone.Therefore, gynecomastia is more common in men over 50.
Other factors include the use of anabolic steroids, as well as certain health conditions, including liver and kidney disease, thyroid disease, hormonally active tumors, and Klinefelter syndrome.
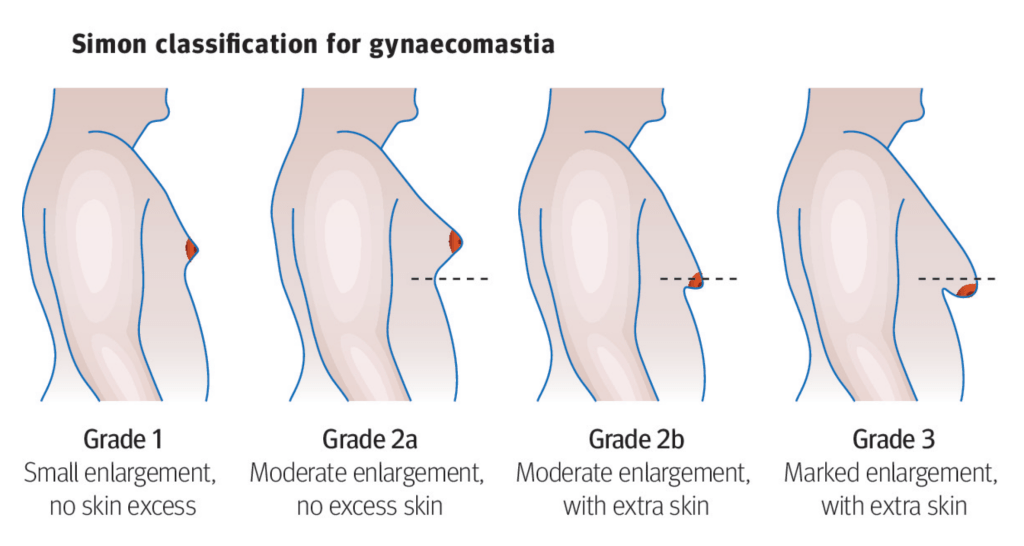
Treatment for Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia has few physical complications, but it can cause psychological or emotional distress. In some cases, especially in the earlier stages, diet and exercise may help manage gynecomastia. In some cases, however, you may need surgery. Your doctor may recommend the following procedures:
- Liposuction (removal of extra breast fat): If gynecomastia is primarily a result of breast fat, liposuction alone may be used. This involves the insertion of a thin hollow tube through a small incision of about 0.5cm, which removes the excess fat from the body by vacuum suction. The procedure takes about 1.5 hours.
- Mastectomy (removal of breast gland tissue): For cases where gynecomastia is a result of both excess breast fat and breast gland tissue, mastectomy may be performed following liposuction. An incision of about 1cm is made on the edge of the areola to remove glandular breast tissue. It takes about 2 hours (including liposuction).
Tumescent local anesthesia is used for the above procedures. It is a technique in which a dilute local anesthetic solution is injected into the subcutaneous tissue, until it becomes firm and tense.
Male breast reduction results are meant to be permanent. However, it’s important to maintain a healthy lifestyle after treatment to prevent a recurrence.
Recovery After Surgery
- To reduce the risk of bleeding and hematoma, you are advised to wear a compression dressing and specially designed pressure garment for 24 hours after surgery. If there is no sign of bleeding afterwards, it is advised to wear the pressure garment for 1-4 weeks after surgery to minimise swelling.
- In some cases, you may need a small, temporary tube that will help to drain off fluid or blood that collects within the chest. Our medical team will explain and demonstrate to you in detail after the surgery.
- Within one month after the surgery, you should avoid exercises such as chest expansion and push-up to help wound healing.
You should seek medical advice before beginning any treatment.
